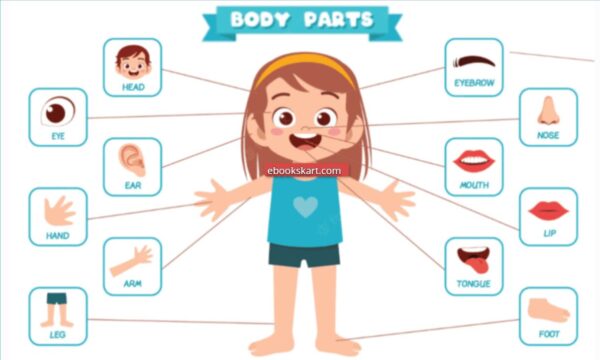
Kids should be aware of the typical body parts names such as head shoulders, knees, toes and more. The goal for this piece is to help children understand the 100+ body parts of the human body names and their roles. Students can download the human body’s parts names PDF free of charge along with a sample image of female and male organs.
The children become more interested in their body Parts Names and how their body functions when they grow. The children have a basic understanding of the body parts that they can observe and understand their function. Children are familiar with the names for the common body parts like the shoulders, head and knees.
What are the other crucial Names of Body parts? The small body parts which make up each major body part serve different purposes. Check out All Body Part Names that are present within the Human Body.
Body Parts Name
If your child is now able to demonstrate a basic understanding of their surroundings and the world around them, it’s time to introduce them to about body components in English. It is essential that children learn the names of each body part as it’s essential to their education. The human body is made up of 30-40 trillion cells, which generate around 242 billion new cells every day. When a particular group of cells join together and create tissues.
Organs are formed by the joining of tissues or body parts. They are then joined to form organ systems and, eventually the whole organism. This article lists an overview of Body Parts Names together with the description of each component’s principal purpose. The goal is to teach youngsters on the names of various body parts, helping them to increase their vocabulary and increase their knowledge of their bodies.
Parts of Body Name
The human body has a variety of organs or body parts which are inside our body. They function to live a healthy and happy life. Our body is comprised of numerous organs and together form a system known as the organ system. Organs and body parts cooperate to aid us in completing our everyday tasks. Based on the criteria used by scientists the body’s organs are classified into three categories which are the torso, external parts, and internal ones. Students can find their body components for each of these groups here.
Body Parts Name With Picture
This article we’ll be able to learn about every body part of the body and the roles that each part of the body does.
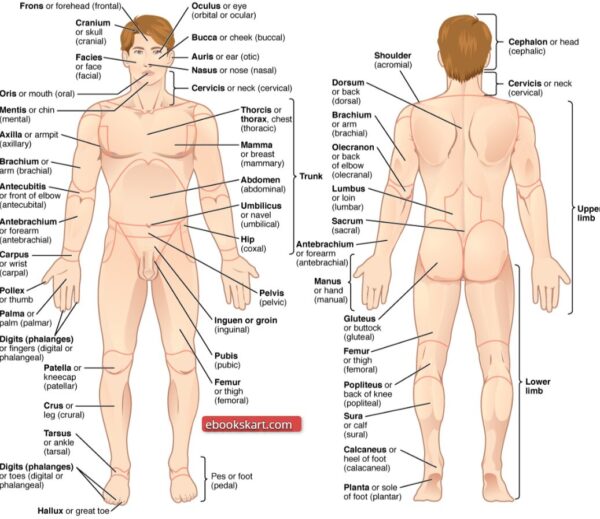
Female Body Parts of Human Named Female with a Photo
The body parts names of females is similar with male body parts’ names. There is a slight difference in the name of body parts of female and male. To aid students in understanding this distinction we have provided male body part’ names as a photo.
All Body Parts Name in English: boNddii paartts nem in Hindi
Here are a list of nearly every body part name that every student should know.
Names of Body Parts Chart
- Hair – baal – [Baal]
- Eyes – aaNkheN – [Aankhen]
- Mouth – muNh – [Munh]
- Arm – baaNh, bhujaa – [ Baanh , Bhujaa]
- Tooth, Teeth – daaNt – [Daant]
- Back, Waist – kmr, piitth – [Kamar , Peeth]
- Shoulder – kndhaa – [Kandha]
- Stomach – pett – [Pet]
- Knee – ghuttnaa – [Ghutana]
- Throat – glaa – [Gala]
- Leg – ttaaNg – [Taang]
- Hand – haath – [Haath]
- Nose – naak – [Naak]
- Ear – kaan – [Kaan]
- Eye – aaNkh – [Aankh]
- Foot – pair – [Pair]
- Head – sir – [Sir]
- Face – cehraa – [Cheharaa]
- Smiley Face – hNsmukh – [Hansmukh]
- Neck – grdn – [Gardan]
- Beard – daarhii – [Daadhi]
- Moustache – muuNch – [Munchh]
- Hip – kuulhaa – [Koolhaa]
- Nail – naakhuun – [Naakhoon]
- Skin – tvcaa, khaal – [Twacha , Khaal]
- Fist – mutthtthii – [Muthhee]
- Lip – hoNtth – [Honth]
- Blood – rkt – [Rakt]
- Brow BHAUNH – bhauNhBrow – bhauNh – [Bhaunh
- Breast – stn – [Stan]
- Elbow – kohnii – [Kohanee]
- Nipple – stn kaa aglaa bhaag
- Navel – naabhi – [Naabhi]
- Armpit, Womb – bgl, kaaNkh – [Bagal , Kaankh]
- Chin – tthuddddii – [Thuddee]
- Forehead – maathaa – [Maathaa]
- Cheek – gaal – [Gaal]
- Ankle – ttkhnaa – [Takhanaa]
- Brain – dimaag – [Dimaag]
- Face – cehraa – [Cheharaa]
- Eyebrow – BhauN – [BhaunBhaun
- Eyelid – plk – [Palak]
- Tongue – jiibh – [Jeebh]
- Heart – Hrdy – [Harday]
- Toe – pair kii uNglii – [Pair Ki Ungalee]
- Body – Shyir – [ShareerShareer
- Fingers – aNguliyaaN – [Unguliyaan]
- Thumb – aNguutthaa – [Angootha]
- Intestine – aaNt – [Aant]
- Heel – Eddh’ii [AidheeIdhee
- Larynx – kNtth – [Kanthh]
- Temple – knpttii – [Kanpati]
- Wrist – klaaii – [Kalai]
- Skull – Khopdd’ii [KhopadeeSkull – khopdd’ii – [Khopade
- Kidney – gurdaa – [Gurdaa]
- Knee – ghuttnaa – [Ghutana]
- Chest – chaatii – [Chhatee]
- Jaw – jbdd’aa – [Jabadaa]
- Thigh – jaaNgh – [Jhaangh]
- Liver – jigr – [Jigar]
- Joint – jodd’ – [Jod]
- Nostril – nthunaa – [Nathoonaaa]
- Nerve, Vein – ns – [Nas]
- Paw – pNjaa – [Panjaa]
- Rib – pslii – [Pasalee]
- Lung – phephdd’aa – [Fefadaa]
- Muscles – maaNspeshii – [Maaspeshee]
- Spine – Riddh’ [Reedhh]
- Bone – hddddii – [Haddee]
- Palm – hthelii – [Hatheli]
- Belly – Pett – Pet
- Calf – piNddlii – [Pindalee]
- Uterus – grbhaashy [Garbhashya]
- Rump cutdd [ChutadChutad
- Bun – baaloN kaa juuddaa [Balon ka Jooda]
- Index Finger – trjnii [Tarjani]
- Palate – taalu [Taalu]
- Snout – Thuuthnaa [Thuthana]
- Molar Theeth – daaddh’ [Daadh]
- Artery – Dhamani – dhmnii
- Pulse – naadd’ii [Naadi]
- Spleen – tillii [Tilli]
- Bile – pitt [Pitt]
- Eyeball – netrgolk, aaNkh kii putlii [ Netragolak]
- Eyelash – Braunii [Barounee]
- Embryo – bhruunn [bhoorn]
- Middle-Finger – Biic kii uuNglii”beech Ki Unagli”
- Urinary Bladder – muutraashy [Mootrashay]
- Saliva – laar [Laar]
- Trachea – svaas nlii, kNtthnaal [Swas nali]
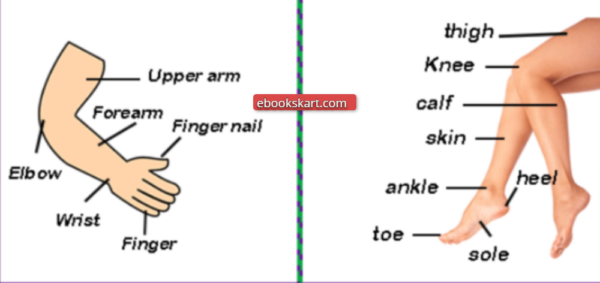
The Extremities Body Part Name
Human body’s legs as well as arms are often referred to as extremities. The elbows, shoulder palms, fingers and wrists of the human arm could be further broken down. The knees, thighs feet, and calves are the other components part of legs. Human body’s arms and legs are comprised of all these parts. The legs are mostly used to move, while the arms aid in taking food items, carrying them and balancing things. Moving from one place to another is often referred to as locomotion.
Internal Organs Body Parts Name
Organs that are easily visible are the organs of our body that were mentioned previously. But, it’s fascinating to know that the human body is a host of organs that aren’t visible for us to easily see, but carry out important functions that ensure our daily lives. Internal organs are in simple terms, body organs which are within the body’s cavity. Internal organs include, but include but are not limited to kidneys, the liver brain, heart, lungs and stomach. Let’s take a look at some of the crucial tasks that the organs inside perform.
The Human Body and the Parts of it as well as Their function
Liver It is considered to be the most important organ that can be found in the human body. It eliminates toxins from the blood supply of the body and also maintains normal glucose levels in the blood, controls blood clotting, as well as performing numerous other vital tasks. It’s located under the rib cage, in the right upper abdomen.
Kidney Human body is composed of two kidneys that are shaped like beans. They are essential to the life of human beings. They help in the production of urine and purifying blood.
Heart The heart is situated in the body’s ribcage. The heart is an organ which functions continuously from the moment of birth. The blood is circulated throughout the body through the heart. Kids can listen to their heart beating in their chests.
BrainThe most important organ in the body of a human being is called the brain. This organ that runs throughout the body. The brain is responsible for everything from remembering to storing information.
Stomach Stomach is muscular organ which digests food using enzymes and acids, beginning the process of digestion. The internal organs of the stomach which include the gastric mucosa, as well as the pyloric sphincter are vital to ensure proper digestion and nutrients intake.
Intestines The intestines which comprise the large and small intestines, are responsible for absorption of nutrients and elimination of waste. Villi and microvilli inside the small intestine increase the surface area to facilitate intake of nutrients, while the large intestine is able to reabsorb water and produces stool.
Pancreas The pancreas plays a significant component that is part of our digestive system. It is responsible for controlling the blood sugar level. The pancreas organ is located within the abdomen. It is a vital part in the process of converting food that we eat into fuel to cells in the body. The pancreas is a major organ with two functions: an exocrine one which aids digestion, and an endocrine function which manages blood sugar.
Lungs The lungs are vital respiratory organs, playing crucial roles in supplying oxygen to blood and eliminating carbon dioxide. The lungs’ alveoli are small air sacs that are which are responsible for gas exchange are crucial for breathing properly. The names of the internal organs like the diaphragm and bronchi are of significance, since they are key to the functioning of the respiratory system.
50 Body Parts Name In English
Here are 50 body parts of the human body. From head to foot:
- Head
- Hair
- Forehead
- Eyebrow
- Eyelash
- Eye
- Ear
- Nose
- Cheek
- Mouth
- Lip
- Tongue
- Tooth (plural tooth (plural)
- Chin
- Neck
- Shoulder
- Arm
- Elbow
- Forearm
- Wrist
- Hand
- Finger
- Thumb
- Chest
- Breast
- Rib
- Abdomen
- Navel (belly button)
- Hip
- Waist
- Buttocks
- Leg
- Thigh
- Knee
- Calf
- Ankle
- Foot
- Heel
- Toe
- Sole
- Back
- Spine
- Nape
- Waistline
- Hips
- Pelvis
- Shin
- Larynx (voice box)
- Trachea (windpipe)
- Esophagus
These are just a few of the most important body organs However, there are numerous anatomical structures that make up the human body.
Human Body Parts Name Human Body Parts Name
Head
Skull is a protective device for the brain.
Brain Control center of the body
Eyes: Vision
Balance and hearing
Nose: Smell
Mouth: Speaking, eating
Teeth: Chewing
Tongue Speech, Taste
Face: Including cheeks, forehead, and the chin
Neck and Throat
Trachea: Air passageway to the lung.
Esophagus: Food passageway into the stomach
Larynx: Voice box
Torso
Chest: Contains sternum as well as the ribs
Abdomen: Houses digestive organs
Back: Includes vertebral column
Upper Limbs
Shoulder: Also known as the clavicle (collarbone)
Arm: Includes upper arm, forearm
Elbow: Joint that connects upper and forearms
Wrist: Joint that connects forearm and hand
Hand: Includes palm, fingers (digits)
Lower Limbs
Hip: Connects the torso to legs
Thigh: Upper portion of the leg
Knee: Joint that connects the lower leg to the thigh
Calf back portion of lower leg
Ankle: Joint linking the foot and leg
Foot: Includes heel, arch, toes
Internal Organs
Heart Pumps blood
Lungs: Breathing
Liver: Detoxification
Kidneys Filtration of blood
Stomach: Digestion
Intestines: Intake of nutrients
Additional Structures
Skin: The largest organ that protects and covers the body
Blood vessels: Include arteries, veins, capillaries
These are the complete human body’s parts names that are present in Human Body.
The Complete List of Parts of Human Body with Information
Overview of the most important human body components and their roles, classified into various systems to better understand:
Skeletal System
Skull – Protects brain and helps support the facial structure.
Spine/Vertebral Column A flexible column that shields the spinal cord and offers structural support for the body.
Ribs protect the lungs and the heart which are an integral part of the thoracic.
Pelvis – It supports your upper body’s weight and offers an attachment point for lower legs.
Bones (206 total) They provide the structure, allow movement and also produce blood cells. Examples include:
Femur (Thighbone) The longest and most durable bone in the human body.
Humerus – Upper arm bone.
Tibia – The bigger and more robust one of two legs bones that are below the knee.
Muscular System
Biceps located within the arm’s upper part and responsible to lift the forearm.
Triceps – located at the back of the upper arm, it assists to straighten the arms.
Quadriceps are the muscles of the front thigh that aid when running, walking and jumping.
Hamstrings – back of the thigh; aid in stretching the knee.
Deltoid – Shoulder muscle which aids in arm rotation as well as lifting.
Nervous System
Brain – The brain’s control center that controls all bodily functions such as thinking, sensation and movement.
Spinal Cord – Transmits messages between the brain and the other parts part of your body.
Nerves – A network of fibers that transmit signals to from various body organs.
Neurons – Specialized cells which deliver nerve signals.
Circulatory System
Heart Pumps circulation of blood through the entire body providing nutrients and oxygen.
Blood Vessels (Arteries Veins, Capillaries, Veins) carry blood from and to the heart.
Aorta – The biggest arterial vein that transports oxygen rich blood to other parts of your body.
Vena Cava, the biggest vein that is responsible for carrying oxygen-deficient blood back to the heart.
Blood – Made up by the red blood cells (carry oxygen) and white blood cells (fight infections) as well as platelets (clotting) and plasma.
Respiratory System
Lungs – The primary organ that regulates gas exchange. oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released.
Trachea (Windpipe) connects the throat and lung, allowing air to flow through.
Diaphragm – Muscle which aids in breathing by relaxing and contracting to increase lung volume.
Bronchi – Two tubes of immense size that transport air through the trachea and to the lungs.
Digestive System
Mouth – The point of entry of digestion. Food particles are broken down through saliva and chewing.
Esophagus Tube – Tube that carries meals from your mouth into the stomach.
Stomach – Secretes acids as well as enzymes that help break down food.
Small Intestine is where the most absorption of nutrients takes place.
The Large Intestine (Colon) It absorbs water and then forms an inorganic and solid waste (feces).
Liver – Produces Bile, aids with digestion, decontaminates chemicals and also metabolizes drugs.
Pancreas – Produces insulin and digestive enzymes.
Gallbladder – Stores bile made in the liver.
Urinary System
Kidneys Filter blood to remove excessive fluid and waste. creating urine.
Ureters are tubes that carry urinary fluid from kidneys into the bladder.
Bladder stores urine until it is removed from the body.
Urethra Urethra Tube via which the urine escapes the body.
Endocrine System
Pituitary Gland – Master gland which regulates other endocrine glands as well as regulates development and growth.
Thyroid Gland regulates the body’s temperature, metabolism energy and body temperature.
Adrenal Glands Produce hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline that help are used to manage stress.
Pancreas – Produces insulin, regulating blood sugar levels.
Reproductive System
Male:
Testes – Make testosterone and sperm.
Penis – External reproductive organ.
Female:
Ovaries – produce eggs and hormones such as progesterone and estrogen.
Uterus – A fertilized egg implanted in the uterus and develops into an embryo.
Vagina is the birth canal, and the organ responsible for sexual intimacy.
Integumentary System (Skin)
Skin – The largest organ in the body. It guards inner organs; regulates temperature and detects the sensation of touch.
Epidermis is the outermost layer of skin.
Dermis contains hair follicles and sweat glands as well as blood vessels.
Hypodermis: A fat layer beneath the skin.
Lymphatic/Immune System
Lymph Nodes Filter lymph fluid and aid in fighting off infection.
Spleen Filters blood and recycles old red blood cells and assists in fighting infections.
Thymus – Produces T cells, that are vital for the immune system.
Sensory Organs
Eyes – Organs responsible for vision that detect light and relay visual signals into the brain.
Ears – Organs that aid in listening and for balance.
Nose – Detects smells, and helps in breathing.
Tongue is a taste organ aids in manipulation of food as well as speech.
Skin – contains receptors that detect pressure, touch, as well as temperature